
Understanding your pet’s body language is an essential part of being a responsible pet owner. Knowing how to identify and understand the physical signals that our canine friends use to communicate can often reveal valuable information about their current emotional state and comfort level.
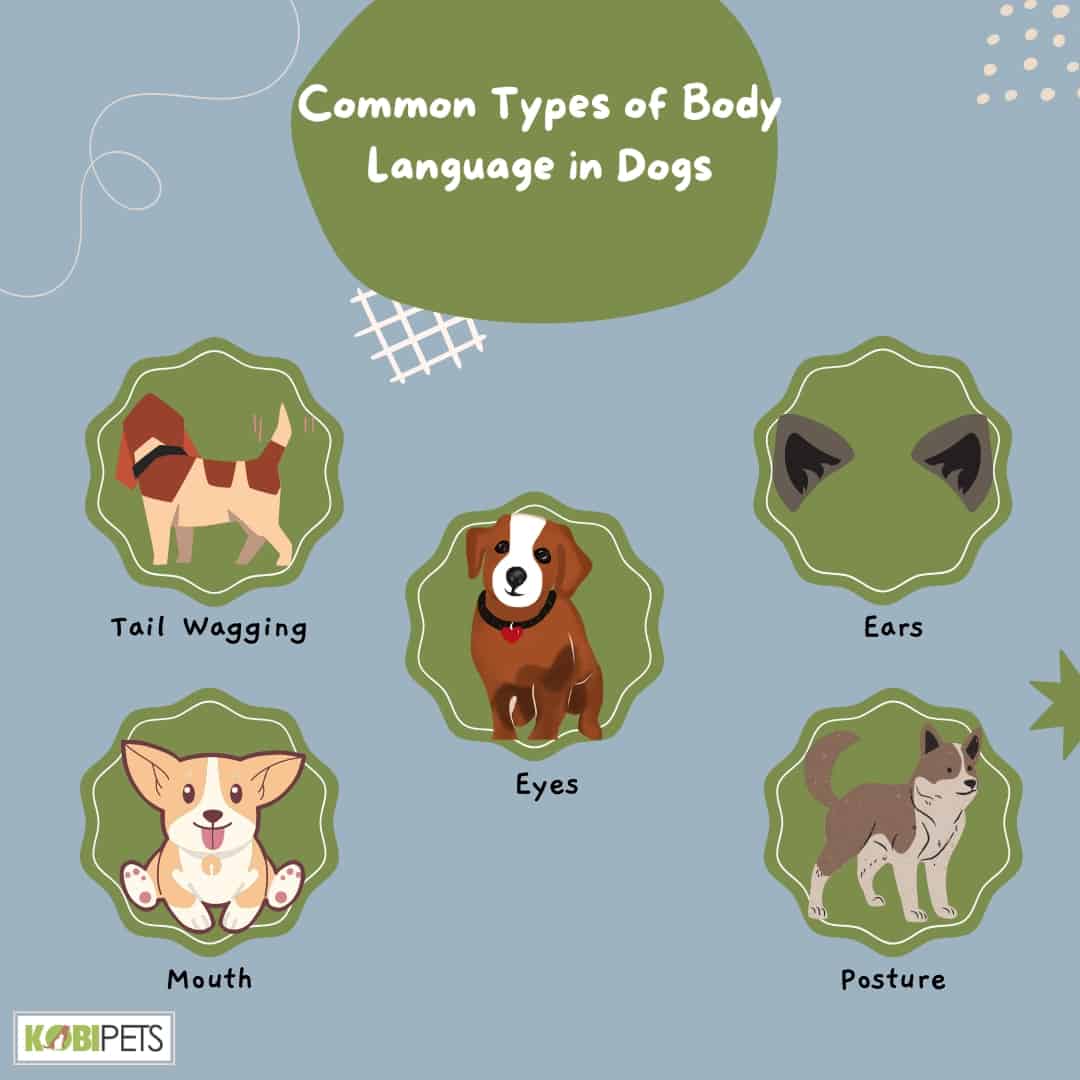
Common types of body language in dogs include tail wagging, facial expressions and eye contact, tail behaviors, posture, vocalizations, and aggressive behavior.
By recognizing the subtle, yet powerful, cues that our furry friends give off, we can start to build meaningful relationships with them and develop bonds of trust between each other.
Importance of Understanding Your Dog’s Body Language
Understanding your dog’s body language is essential for building a strong relationship with your pet and ensuring its safety and well-being.
Dogs primarily communicate through body language, and by understanding what they are trying to convey, you can respond appropriately and avoid misunderstandings.
One of the primary benefits of understanding your dog’s body language is that it allows you to identify signs of stress or anxiety in your pet.
Dogs can become anxious or agitated for various reasons, including fear, excitement, or discomfort.
By recognizing the subtle signs of anxiety, such as lip licking, yawning, or avoidance behaviors, you can take steps to alleviate your dog’s stress and provide them with a more comfortable environment.

Common Types of Body Language in Dogs
Dogs have their own way of communicating with us and other animals around them. Understanding their body language can help us better understand their emotions and intentions. Here are some common types of body language in dogs:
1. Tail Wagging
Tail wagging is often associated with happiness, but it can also indicate other emotions such as fear or aggression. The position and speed of the wag can give clues to the dog’s mood.
2. Ears
Dogs use their ears to express a range of emotions. Erect ears may indicate alertness or aggression, while flattened ears may indicate fear or submission.
3. Eyes
A dog’s eyes can also give clues to its emotional state. Dilated pupils may indicate excitement or fear, while narrowed pupils may indicate aggression.
4. Mouth
A relaxed mouth with an open jaw may indicate a happy or relaxed dog, while a closed mouth with tense lips may indicate stress or aggression.
5. Posture
A dog’s overall posture can also give clues to its mood. A relaxed and loose body posture may indicate comfort and happiness, while a stiff and tense posture may indicate fear or aggression.
Understanding your dog’s body language is an important part of being a responsible pet owner.
By paying attention to these common types of body language, you can better communicate with your furry friend and ensure they feel safe and comfortable in their environment.
Common Types of Body Language in Dogs
Understanding Facial Expressions and Eye Contact
Just like humans, dogs also communicate through nonverbal cues such as facial expressions and eye contact. Understanding these cues can help you better understand your furry friend’s emotions and needs.
Facial expressions are a crucial aspect of dog communication. A relaxed mouth with slightly open lips indicates that your dog is calm and content.
On the other hand, a tense mouth with tightly closed lips may indicate fear or aggression. Similarly, raised eyebrows and wide eyes can indicate excitement or curiosity, while narrowed eyes can signal discomfort or aggression.
Eye contact is another important aspect of dog communication. Direct eye contact from a stranger can make some dogs uncomfortable or even aggressive, while prolonged eye contact from their owner can strengthen the bond between them.

Interpreting Tail Wagging and Other Tail Behaviors
Tail wagging is one of the most well-known dog behaviors, but did you know that it can indicate more than just happiness?
The position and speed of a dog’s tail can give important clues about its mood and intentions.
A high and stiffly held tail usually indicates alertness or aggression, while a low-held tail may indicate fear or submission.
A relaxed and gently wagging tail is often associated with happiness, but a fast and vigorous wag can indicate excitement or even aggression.
In addition to wagging, dogs use their tails for other forms of communication as well. A tucked tail usually indicates fear or anxiety, while a puffed-up tail can signal aggression.
Some breeds also have unique tail behaviors – for example, Basenjis do not bark but instead communicate through yodels and curly tails.

Posture and Body Position
Just like humans, dogs also have their own way of communicating through body language. One of the key components of a dog’s body language is its posture and body position.
Understanding what your dog’s posture and body position mean can help you better communicate with them and ensure their overall well-being.
A dog’s posture refers to the position in which they hold its body while standing, sitting, or lying down. A confident dog will typically stand tall with their head held high and ears perked up.
On the other hand, a fearful or submissive dog may crouch down with their tail tucked between its legs.
Body position also plays an important role in a dog’s communication. For example, a relaxed and content dog will often lie on their side with all four legs stretched out.
However, if a dog is feeling threatened or defensive, it may stand with its front legs slightly forward and its weight shifted towards the back legs.
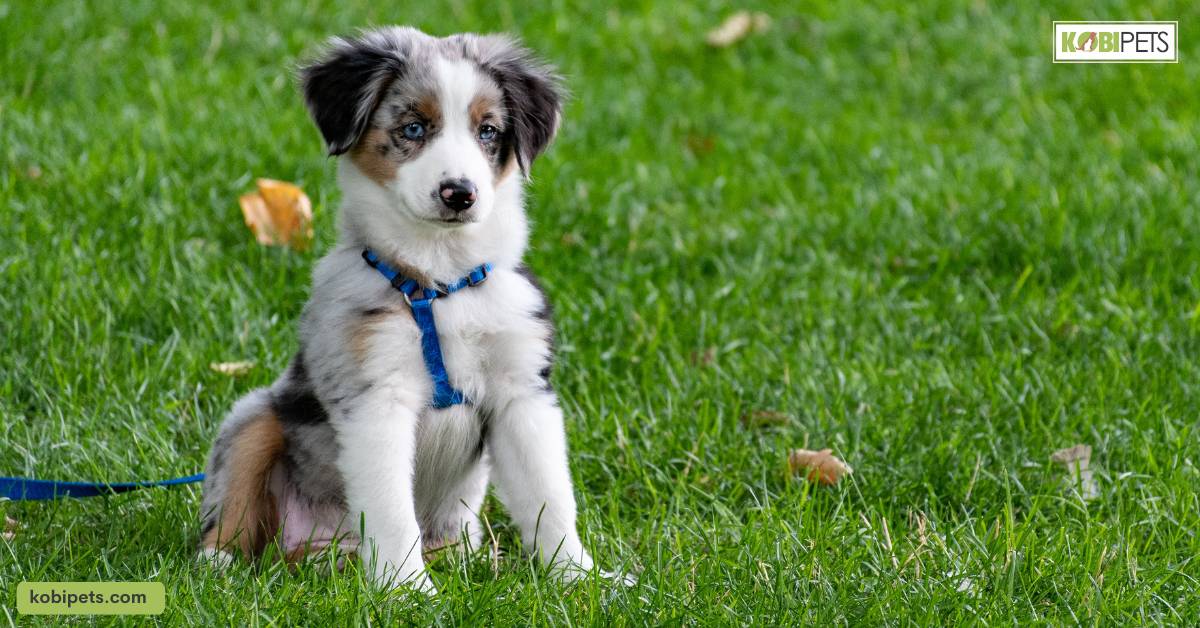

Vocalizations and Sounds
While dogs primarily communicate through body language, they also use vocalizations and sounds to convey their emotions and intentions.
Understanding what your dog’s different vocalizations mean can help you better communicate with them and ensure their well-being.
One of the most common vocalizations that dogs make is barking. Dogs bark for a variety of reasons, including to alert their owners of potential danger or to express excitement or playfulness.
However, excessive barking can be a sign of anxiety or stress.
Whining is another common vocalization that dogs make. This can indicate a wide range of emotions, from excitement to fear or pain.
Yapping is similar to barking but tends to be higher-pitched and more repetitive.
Growling is a sound that many people associate with aggression in dogs, but it can also indicate fear or discomfort.
It’s important to pay attention to your dog’s body language when they are growling to determine the underlying cause.
Other sounds that dogs may make include howling, which is often associated with loneliness or separation anxiety, and whimpering, which can indicate pain or distress.
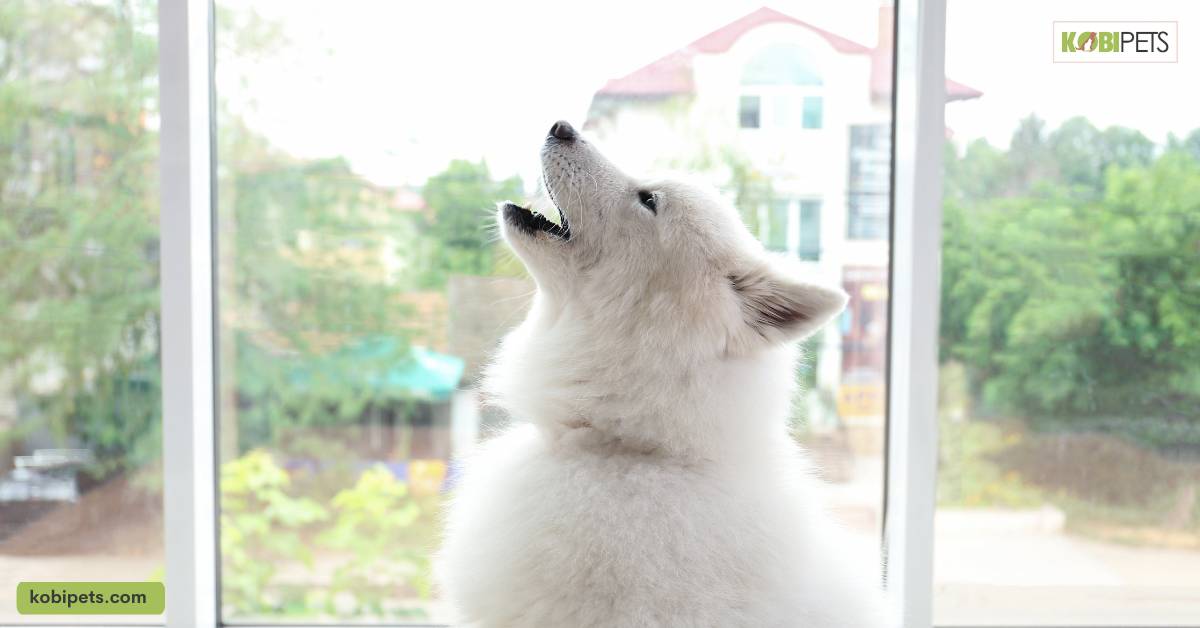

Understanding Aggressive Body Language in Dogs
Understanding your dog’s body language is crucial for building a strong bond with your furry friend. It allows you to communicate effectively and respond appropriately to their needs and emotions.
However, it’s equally important to recognize aggressive body language in dogs to prevent any unwanted incidents.
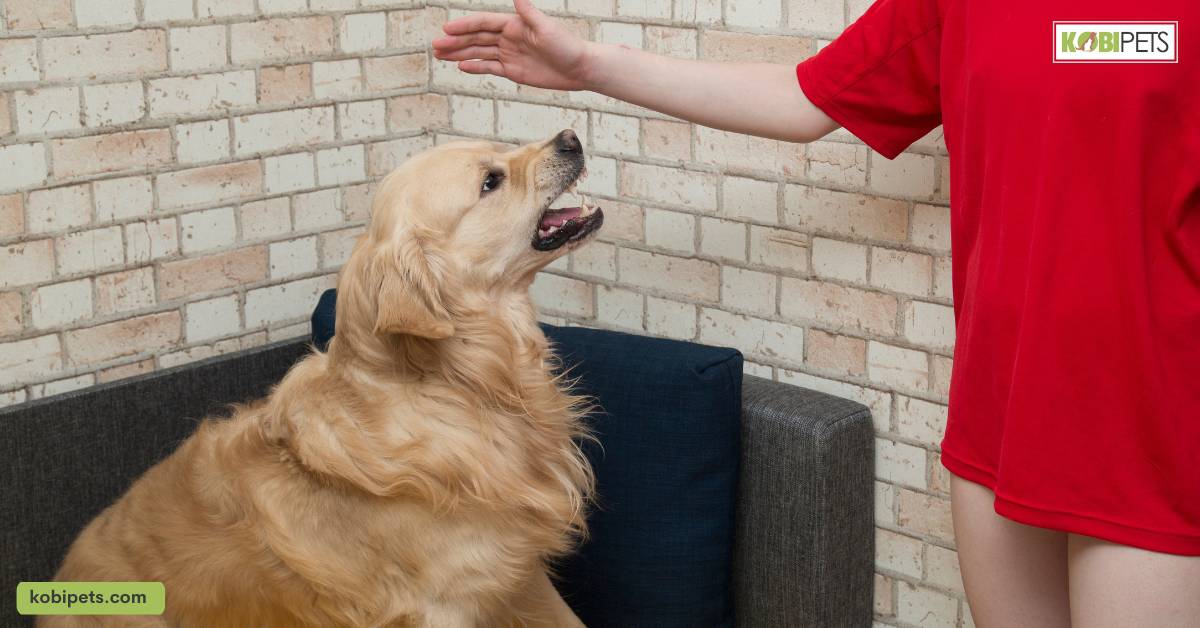
Some common signs of aggressive body language in dogs include a forward-leaning stance, stiff body, tail above the horizon (possibly stiff or wagging), ears up and forward, and intense eye contact.
These signals indicate that the dog is feeling threatened or uncomfortable and may attack if provoked.
It’s essential to note that not all dogs display aggressive behavior in the same way. Some may growl or bark, while others may show their teeth or bite without warning.
Therefore, it’s crucial to observe your dog’s body language carefully and seek professional help if you notice any concerning behavior.

In conclusion
Being able to understand your dog’s body language is an important skill that all owners should have. It can help owners get to know and better understand their pets, communicate effectively with them, and create a stronger bond between the two of them.
Additionally, it will enable you to recognize signs of aggression in other dogs and avoid potentially dangerous situations. Therefore, take some time to study the topic and spend more time observing the behavior of your own pet.






